The rate of Vietnamese women with dense mammary glands is often higher than those in Europe and America, making the risk of breast cancer is also 4-6 times higher. However, a good news is that artificial intelligence (AI) is now able to determine the breast density, serving the early diagnosis and screening of cancer.
The mammary gland has three basic components including connective fibrous tissue, parenchyma and fat. Doctors can determine four types of breast parenchymal density based on X-rays. Accordingly, while 80% of American women have an intermediate breast density between fat and fibroids; in Vietnam, due to small stature and less obesity, the proportion of women with dense breasts (mostly fibroids) is often higher, increasing the risk of related cancers. According to WHO statistics, by 2020, Vietnam has 21,555 new cases of breast cancer, of which 70% are detected late, significantly increasing the mortality rate.
Currently, according to the US Food and Drug Administration FDA, a mammogram is the only screening method that reduces mortality from breast cancer. X-rays can show calcifications and masses, which are the first typical symptoms of cancer. This method is therefore used both in diagnosis and screening, to screen a large area when the patient has no specific symptoms or to observe more clearly.
AI determines the density of parenchyma and localized breast lesions
From the practical use of X-rays in mammary structure imaging, for early detection of cancer cells, scientists from Vingroup Big Data Institute (VinBigdata) have researched and developed VinDr-Mammo. This is one of the seven modules of VinDr – a comprehensive solution for medical image analysis that integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI) into a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) to assist radiologists in making fast and precise diagnoses.
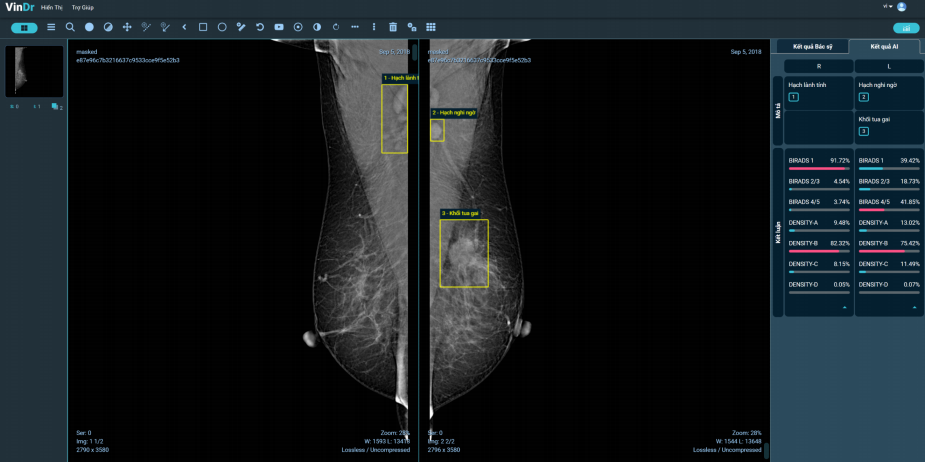
To be able to perform multi-tasking on mammograms, VinDr-Mammo is trained from 50,000 studies collected at major hospitals in the country. Before being put into machine learning training, data will be “de-identified” and stored on the Label-PACS system for remote access and being labeled by doctors. In addition, in terms of core technology, the software is also built from advanced technologies of artificial intelligence, including computer vision, deep learning, image analysis, Computer aided detection and Computer aided diagnosis.
As a result, VinDr-Mammo can classify the density of the parenchyma, as well as localize 13 different types of lesions on a mammogram, with an average accuracy of over 85% and diagnosis time less than 05 seconds per scan.
When put into operation at the hospital, VinDr-Mammo will work as an assistant providing an additional objective opinion for the radiologists before delivering final results. In fact, trials at major domestic hospitals (108 Hospital, Hanoi Medical University Hospital, Vinmec Times City Hospital and 05 other ones in Phu Tho province) showed that, on average, over 10% of the diagnosis cases changed the results after the doctor consulted AI. Along with that, the average consensus of AI with doctors also reached 84% (at Hanoi Medical University Hospital).
AI supports BIRADS classification, paving the way for large-scale breast cancer screening
BIRADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System) is a system to classify mammogram results according to the available scale. In which, BIRADS 1 shows no lesions; BIRADS 2 and 3 are more probably normal, but there’s a 2 percent chance of cancer. From BIRADS 4-6, the probability of a malignant tumor gradually increases (31-97%). This is one of the first bases for a doctor to decide whether to perform a biopsy to determine breast cancer or not.
Currently, with AI, VinDr-Mammo is able to classify BIRADS on a mammogram, aiming to accurately screen cancer risk. Furthermore, the software’s outstanding advantage is its ability to automatically diagnose multiple cases simultaneously with constant speed and accuracy, while each doctor can only read an image at a time. Combined, this is expectedly the solution to large-scale breast cancer screening, while meeting the need to store and transmit large-scale medical image data sets, with two-way integration into medical digital applications such as HIS / RIS / EMR / PACS, etc.
Along with the detection of breast lesions and diseases, VinDr also has other diagnostic modules including Brain CT interpretation; Chest X-ray interpretation; Abdomen CT interpretation; Bone X-ray interpretation; Brain MRI interpretation and Chest CT interpretation. With the above features, VinDr aims to become a reliable medical imaging assistant for doctors, contributing to improving the quality of medical examination and treatment.












