Lung cancer ranks 2nd among the most common cancers in Vietnam. With the ability to diagnose multiple cases simultaneously, at constant speed and accuracy and not limited by time or space, the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) – VinDr can therefore support large-scale screening.
According to the latest statistics of the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IACR, under WHO), by 2020, Vietnam would up 7 places on the world cancer map. Specifically, our country ranks 92 out of 185 countries and territories, with a rate of 159.7 per 100,000, ranking 16th in Asia and 6 in Southeast Asia. In particular, Vietnam is one of the 50 countries with the highest cancer death rate in the world (106 / 100,000 people).
Lung cancer is one of top killers to Vietnamese people. Similar to the global general situation, in Vietnam, lung cancer, with 26,262 new cases and 23,797 deaths in 2020, was ranked 2nd among the most affected cancers in Vietnam for both genders. It is worth mentioning that up to 25% of lung cancer patients are diagnosed late, making it difficult for treatment.
Early diagnosis with various lesions
For gradually solving the lung cancer issue, the key is to increase the number of early diagnosis cases. One of the hallmarks of lung cancer is an infection that affects the respiratory tract and leads to diseases like bronchitis or other chronic infections. The chronic lung infections can be completely diagnosed early by using chest X-rays to localize the lesion. Therefore, currently chest X-ray is the first step for doctors to detect abnormalities before deeper interventions such as computed tomography (CT chest) or biopsy.
As the above fact, scientists of Vingroup Big Data Institute (VinBigdata) have put into the trial operation VinDr-ChestXR since June 2020. It is one of seven modules of VinDr – a comprehensive solution for medical image analysis that integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI) into a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) to assist radiologists in making fast and precise diagnoses.
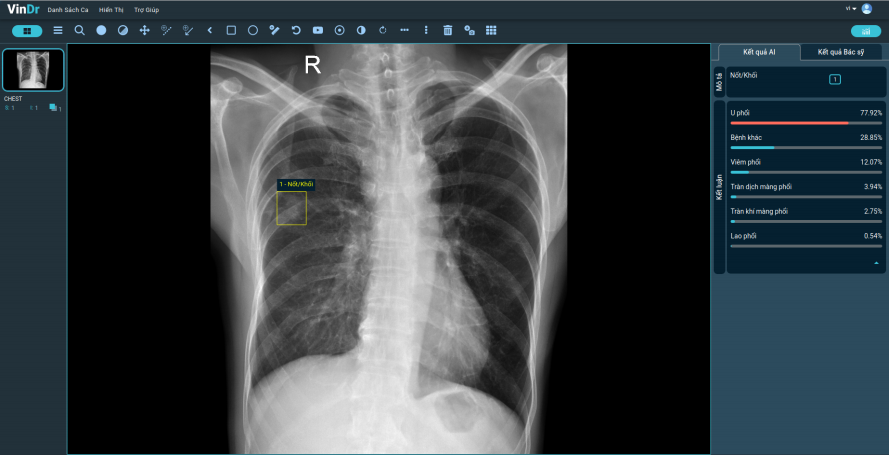
To be able to localize and classify a variety of lesions, VinDr-ChestXR is trained from more than half a million lung X-ray studies and nearly 300,000 scans in the community, especially leading Vietnamese hospitals. Collected data will then be “de-identified” and stored on the Label-PACS system for remote access and being labeled by doctors. The final result is for machine learning training. In addition, in terms of core technology, the software is also built from advanced technologies of artificial intelligence, including computer vision, deep learning, image analysis, Computer aided detection and Computer aided diagnosis.
Thus, with VinDr-ChestXR, the AI-assisted diagnostic system can detect 06 lung diseases and localize 22 common abnormalities on chest X-ray images. This is an important prerequisite step to determine the risk and progress of lung cancer in patients.
Large-scale lung cancer screening
According to statistics in 2020, Vietnam had an average of 1 doctor per 1,000 people, indicating hospital overload and enormous pressure on the medical system. Moreover, this human resource is unequally distributed among regions, leading to an increasing disparity in the quality of medical examination and treatment between rural and urban areas.
Artificial intelligence, with the collaboration of hundreds of leading doctors in the country, will become the solution to this problem. Thus, applying VinDr-ChestXR will help narrow the gap in the quality of cancer diagnosis between higher and lower level hospitals. Moreover, unlike doctors who only read each case in turn during their work time, the outstanding advantage of VinDr-ChestXR is the ability to automatically diagnose multiple cases simultaneously, working at a high speed and constant accuracy without any space or time limitation. In less than 1 second, the system was able to detect 28 common lung lesions and diseases. This is the key to reduce the overcrowding of the medical staff, thereby paving the way for a large-scale lung cancer screening.
High rate of accuracy
Implementing VinDr-ChestXR in the hospital is feasible, because artificial intelligence will not completely replace the role of the radiologist, but will provide an additional opinion for doctors to refer after reading the image. In other words, the system will be a powerful support tool, a consultant for doctors. Therefore, the application of VinDr-ChestXR means an increase in the accuracy level in disease diagnosis.
In fact, VinDr-ChestXR has been tested in major hospitals in Vietnam: 108 Hospital, Hanoi Medical University Hospital, Vimec Times City Hospital and 05 other ones in Phu Tho province. Evaluation results show that at 108 Hospital, an average of 10.5% of diagnoses changed after the doctor consulted AI, the average consensus of doctors with AI also reached 90.5%. This result was similar to that at Hanoi Medical University hospital, with the rates of 4.8% and 89.5% respectively. On average, the diagnosis accuracy of VinDr-ChestXR’s lung diseases was over 90%.
Besides VinDr-ChestXR, the system also has another feature that can diagnose lung cancer, namely VinDr-ChestCT for Chest CT interpretation. Currently, VinDr-ChestCT has been completed and will soon be put into trial implementation in hospitals. These modules promise to thoroughly and comprehensively solve the problem of early diagnosis of lung cancer for Vietnamese people.
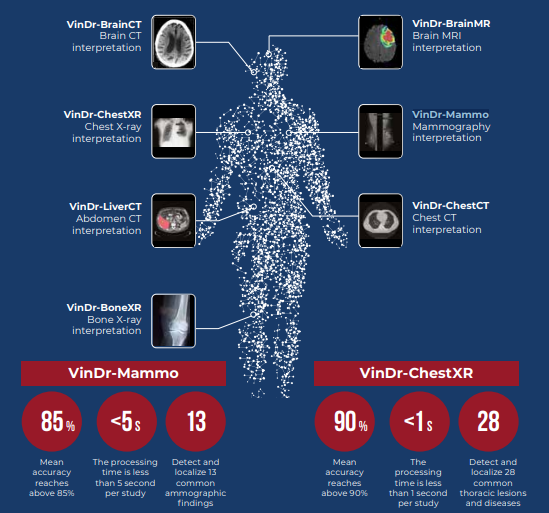
Along with the detection of lesions and lung diseases, VinDr has many other modules, including: VinDr-BrainCT; VinDr-LiverCT; VinDr-BoneXR; VinDr-BrainMR and VinDr-Mammo. With the above features, VinDr aims to become a reliable medical imaging assistant for doctors, contributing to improving the quality of medical examination and treatment.
In addition to building VinDr solutions, from December 31, 2020 to March 31, 2021, VinBigdata organized Chest X-ray Abnormalities Detection on Kaggle, to provide a data set of 18,000 Vietnamese medical images for the domestic and foreign scientific community to develop solutions to Vietnamese health problems. See more details of the contest here.
The rate of Vietnamese women with dense mammary glands is often higher than those in Europe and America, making the risk of breast cancer is also 4-6 times higher. However, a good news is that artificial intelligence (AI) is now able to determine the breast density, serving the early diagnosis and screening of cancer.
The mammary gland has three basic components including connective fibrous tissue, parenchyma and fat. Doctors can determine four types of breast parenchymal density based on X-rays. Accordingly, while 80% of American women have an intermediate breast density between fat and fibroids; in Vietnam, due to small stature and less obesity, the proportion of women with dense breasts (mostly fibroids) is often higher, increasing the risk of related cancers. According to WHO statistics, by 2020, Vietnam has 21,555 new cases of breast cancer, of which 70% are detected late, significantly increasing the mortality rate.
Currently, according to the US Food and Drug Administration FDA, a mammogram is the only screening method that reduces mortality from breast cancer. X-rays can show calcifications and masses, which are the first typical symptoms of cancer. This method is therefore used both in diagnosis and screening, to screen a large area when the patient has no specific symptoms or to observe more clearly.
AI determines the density of parenchyma and localized breast lesions
From the practical use of X-rays in mammary structure imaging, for early detection of cancer cells, scientists from Vingroup Big Data Institute (VinBigdata) have researched and developed VinDr-Mammo. This is one of the seven modules of VinDr – a comprehensive solution for medical image analysis that integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI) into a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) to assist radiologists in making fast and precise diagnoses.
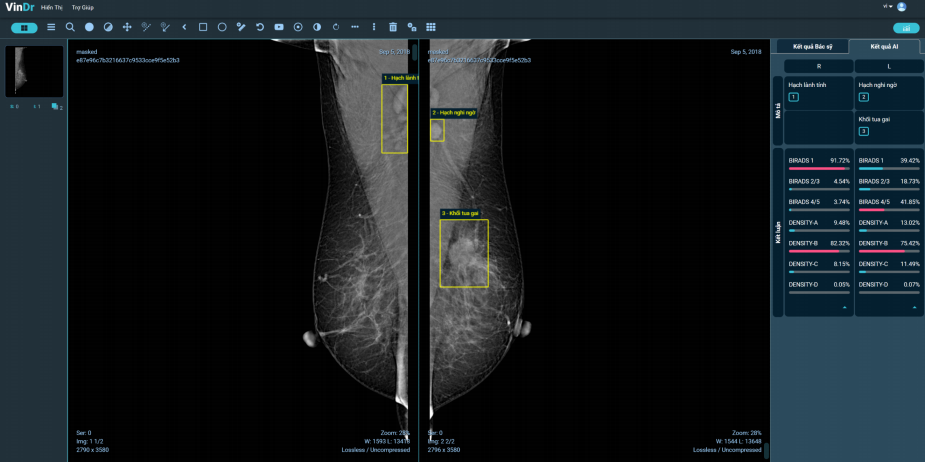
To be able to perform multi-tasking on mammograms, VinDr-Mammo is trained from 50,000 studies collected at major hospitals in the country. Before being put into machine learning training, data will be “de-identified” and stored on the Label-PACS system for remote access and being labeled by doctors. In addition, in terms of core technology, the software is also built from advanced technologies of artificial intelligence, including computer vision, deep learning, image analysis, Computer aided detection and Computer aided diagnosis.
As a result, VinDr-Mammo can classify the density of the parenchyma, as well as localize 13 different types of lesions on a mammogram, with an average accuracy of over 85% and diagnosis time less than 05 seconds per scan.
When put into operation at the hospital, VinDr-Mammo will work as an assistant providing an additional objective opinion for the radiologists before delivering final results. In fact, trials at major domestic hospitals (108 Hospital, Hanoi Medical University Hospital, Vinmec Times City Hospital and 05 other ones in Phu Tho province) showed that, on average, over 10% of the diagnosis cases changed the results after the doctor consulted AI. Along with that, the average consensus of AI with doctors also reached 84% (at Hanoi Medical University Hospital).
AI supports BIRADS classification, paving the way for large-scale breast cancer screening
BIRADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System) is a system to classify mammogram results according to the available scale. In which, BIRADS 1 shows no lesions; BIRADS 2 and 3 are more probably normal, but there’s a 2 percent chance of cancer. From BIRADS 4-6, the probability of a malignant tumor gradually increases (31-97%). This is one of the first bases for a doctor to decide whether to perform a biopsy to determine breast cancer or not.
Currently, with AI, VinDr-Mammo is able to classify BIRADS on a mammogram, aiming to accurately screen cancer risk. Furthermore, the software’s outstanding advantage is its ability to automatically diagnose multiple cases simultaneously with constant speed and accuracy, while each doctor can only read an image at a time. Combined, this is expectedly the solution to large-scale breast cancer screening, while meeting the need to store and transmit large-scale medical image data sets, with two-way integration into medical digital applications such as HIS / RIS / EMR / PACS, etc.
Along with the detection of breast lesions and diseases, VinDr also has other diagnostic modules including Brain CT interpretation; Chest X-ray interpretation; Abdomen CT interpretation; Bone X-ray interpretation; Brain MRI interpretation and Chest CT interpretation. With the above features, VinDr aims to become a reliable medical imaging assistant for doctors, contributing to improving the quality of medical examination and treatment.
Each year, the world has roughly 40 million incorrect medical imaging diagnoses. So how are both the quantity and quality of diagnoses increased? VinDr – an artificial intelligence system that resonates the power of thousands of medical intellectuals and hundreds of thousands of clinical image data, is expected to be the solution.
From the challenging issues
According to research by Fortune Business Insights, the size of the global medical imaging market in 2019 was 33.69 billion USD and is expected to reach 43.33 billion USD by 2027. The market CAGR is estimated at 5.1% throughout the prediction period. The World Health Organization (WHO) also estimates that every year there are about 3.6 billion diagnoses globally. In fact, governments are paying increasing attention to the monitoring and screening of population health, investing in early detection of disease risks to minimize treatment costs. In addition, the increase in the incidence of acute and chronic diseases including cancer, cardiovascular and orthopedic trauma is the main reason driving diagnostic imaging into one of the thriving trends of medicine.
In Vietnam, early and accurate diagnosis for disease detection and treatment is also an urgent issue, requiring serious investment from the government and individuals. The reason is that in 2019, although ranking 99 out of 185 countries in terms of disease incidence (151.4 / 100,000 population), Vietnam ranks 56th in the world in mortality from cancer (104,4 / 100,000) – WHO reported. According to experts, the cause of this condition is that more than 70% of cancer cases are detected and treated late. If diagnosed early, the treatment effect can be up to 70% as in countries with developed healthcare industry.
This fact raises an urgent requirement: How to improve the quantity, speed and quality of diagnostics? The answer probably lies not only in the human resource factor, because at present, the rate of diagnostic imaging error accounts for 3-5% (about 40 million cases/year globally). Moreover, the overcrowding of cases in hospitals and the shortage of doctors are a big problem for Vietnamese healthcare. So, what resources will assist the doctor in the diagnosis of the disease?
To solution-seeking journey
According to the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), artificial intelligence (AI) will be the leading technology and an effective assistant for radiologists. In terms of speed, AI shortens the time spent on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), as well as image processing and identifying disease. In terms of diagnostic quality, thanks to AI that synthesizes historical factors and compares prognosis with similar cases in the past, patients can get accurate results and personalized treatment regimens from the first time. Because of the above properties, clearly, the answer to the medical imaging problem lies in AI. Instead of waiting for a new generation of medical staff, who are qualified enough to meet the increasing demand of patients in early detection of disease risk, AI will be a fast and durable enough resource to continuously solve medical problems.
Thus, VinDr – a hard-working student having trained by a team of hundreds of radiologists since 2018, has constantly optimized its AI algorithm to produce the fastest and the most precise results. Applying computer vision (CV), machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) models, VinBigdata builds computer-aided diagnostic systems (CADx) from large clinical data sets (including various types of medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, etc). Expected to be a comprehensive AI solution for medical imaging diagnostics, VinDr is developed with seven diagnostic modules, including VinDr-BrainCT; VinDr-ChestXR; VinDr-LiverCT; VinDr-BoneXR; VinDr-BrainMR; VinDr-Mammo and VinDr-ChestCT.

- For chest X-ray, VinDr can identify 6 lung diseases and localize 22 common abnormalities. Trained and validated on half a million chest X-ray studies from both public sources and several hospitals in Vietnam, VinDr-ChestXR achieves over 90% accuracy for most diseases and injuries.
- For VinDr-Mammo, it is able to classify a mammography study into 3 BI-RADS (Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System) levels and 4 types of breast density. The system can also localize 13 types of common abnormalities on mammography. Trained from more than 50,000 studies collected at hospitals in Vietnam, VinDr’s BI-RADS classification accuracy is over 80%.
- For VinDr-BrainCT, it identifies 9 brain diseases, including several types of stroke, and localize 17 types of common abnormalities on brain CT scans. This is the result of training from more than 30,000 studies collected in communities and hospitals in Vietnam.
- For VinDr-BrainMR, with training data set from over 3,000 studies, 09 diseases (including brain tumor) and 20 common abnormalities are the diagnostic results obtained by VinDr.
- Finally, for VinDr-LiverCT, from over 10,000 studies, it helps detect 10 diseases (including liver cancers) and localizes 24 common abnormalities.
In addition to the diagnostic ability, VinDr can also automatically localize a suspected lesion and point out anomalies with an average accuracy of over 90%. Thanks to the above features, VinDr will play the role of objective consultation, making sure not to miss any small details, helping doctors have enough data to make the best decision.
And the recognition of the scientific community
Resonating the power of thousands of medical intellectuals, with being trained from huge data on medical images, VinDr has proven its competencies in prestigious international competitions, as:
- No 1 in CheXpert competition organized by Stanford University in 2019.
- No 1 in Abnormal Image Detection in Endoscopy Videos (EndoCV), 2020.
- Top 3 in Pulmonary Embolism Detection Challenge, organized by the Radiological, Society of North America (RSNA), 2020.
- Top 10 in Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection Challenge on CT scans, organized by the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), 2019.
Assessing VinDr, Dr. Le Tuan Linh, Head of Diagnostic Imaging Department, Hanoi Medical University Hospital said: “Early detection of cancer through imaging plays an important role in successful treatment for cancer patients. The application of AI in this field creates an effective support tool for cancer screening programs or other incurable diseases in the future. We evaluate that the VinDr system can be at the forefront in imaging diagnostic support”.
With these achievements, VinDr is becoming one of the new resources in leading hospitals in Hanoi and Phu Tho. In Hanoi, the solution was applied at 108 Military Central Hospital, Hanoi Medical University Hospital and Vinmec Times City International Hospital. In Phu Tho, 5 provincial hospitals are also implementing VinDr.
Together with VinDr – a comprehensive AI solution for medical imaging diagnostics, VinBigdata also strives to provide the community with a set of advanced technology solutions (including VinBot and VinGen), to answer the popular healthcare issues in Vietnam and worldwide. Not only aiming to promptly and quickly solve the shortcomings of the medical industry, VinBigdata aims to create a sustainable direction for the journey of caring and protecting the health of Vietnamese people.





